EpidemicDrive
This drive covers epidemics - not just the coronavirus but any future epidemics. It explains how epidemics start and happen, how they spread, what people can do about it. It also considers the long term impacts, not only of the epidemic but of the steps taken to deal with them.It's called coronavirus from the word 'corona' which means crown in Latin - it has a series of crown-like spikes on its surface. When the disease affects humans, it is called COVID-19 named as Corona Virus Disease 2019 (the year it was discovered). The virus is also called SARS-COV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2) as coronavirus is related to SARS - much less deadly but more infectious.
Click on a heading below and see a summary, and if you're interested you can GO and read more about it!
Here are some initial thoughts about epidemics. GO!
Here are some facts and stats about epidemics. GO!
Look at past pandemics and their impact. GO!
See exactly what the coronavirus is. GO!
What is the current position with this pandemic. GO!
See show world governments (and ours) reacted to the pandemic. GO!
See what the ‘death rate’ is (and what that means exactly). GO!
Have a look at some things that have changed since 2020. GO!
see both sides of the argument and what YouDriveHealth thinks. GO!
If you’re a visitor to our site you can join and download information, assess your own health and create your own action plans, and even contribute to our site. GO!
See what you can do next. GO!
We have some additional information on this subject. GO!
Some Initial Thoughts
The return of an ancient enemy
Throughout history, nothing has killed more human beings than the viruses, bacteria and parasites that cause disease. Not natural disasters like earthquakes or volcanoes. Not war – not even close. Malaria, spread by mosquitoes, still kills nearly half a million people a year
When compiling the list of pandemics we realised one key thing - we don’t seem to eradicate these viruses totally. Viruses can mutate over time and become even deadlier than before. Often as we have seen in the past very quickly things go back to normal until the virus raises its head again often under the same circumstances.

The years 2020 -2022 have changed our world completely
Media driven hysteria or sensible reaction?
The measures governments took in response to the pandemic and the scenes in Italy with the health service threatening to be overrun have changed the relationship between the governments and the people. Freedoms that have been taken for granted since WWII in most countries were removed, without much protest. Polls suggested that the majority of people were actually in favour of these measures.
There was an unrelenting barrage of media which served the purpose of terrifying the population - whether for good to encourage compliance with necessary steps being taken or for another reason - who knows?
One thing for sure - a lot of 'information' that was reported and which was defended by anyone publicly disagreeing being vilified and excluded has since turned out to be wrong. In EpidemicDrive we wrote that after vaccination people wouldn't get re-infected, and wouldn't be able to pass on the disease. Wrong.
Media which for years has peddled the 'company line', reporting Covid deaths every day, now state that the death toll is 'inaccurate'. Professor Carl Heneghan from Oxford University's Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, said: 'Some of those counted as a Covid fatality may never have had the virus'. He claimed that the death-toll data led to 'an explosion of fear-mongering' online.
See below for more details on these and other aspects.
Facts About Epidemics
4 types of coronavirus cause 15-30% of common colds (SCMP) – the COVID-19 coronavirus is the seventh type identified which affects humans of more than 200 types.
10% of the world’s population are estimated to have died in the Plague of Justinian A.D. 541-542 which racked the Byzantine Empire
The mortality rate for SARS is 9.6% compared to 34.5% for Mers and 0.1% for influenza – COVID-19 is unknown yet (SCMP)
Some estimates suggest that 90% of the indigenous population including Incas and Aztecs in the Western Hemisphere was killed off by the American Plagues (European diseases incl Smallpox) in the 16th century
500,000 is the number of people commonly cited to die of influenza in a given year with no complications (SCMP)
The plague started in April 1665 and spread rapidly through the hot summer months. Fleas from plague-infected rodents were one of the main causes of transmission. By the time the plague ended, about 100,000 people, including 15% of the population of London, had died.
1357 AD was the start of the Bubonic Plague in Europe – it killed 50 million people – a greater &-age of the world’s population than anything else (HistoryExtra)
20% of the estimated 500 million people from the South Seas to the North Pole who fell victim to Spanish Flu died from it (Healthline). It didn’t start in Spain!

The history of pandemics
Here's some information on some of the worst plagues in history. .
The plague of Justinian 541-542 named after the Byzantine Emperor Justinian (reigned A.D. 527 - 565) - this was the bubonic plague and it started the decline of the empire. Estimates suggest 10% of the world's population died.
The Black Death 1346-1353 brought from Asia to Europe and spread by fleas on rats, some estimates suggest it killed half of Europe's population. It changed the course of history - with so many workers dead technical innovation increased and working conditions improved.
Cocoliztli Epidemic 1545 - 1548 this was a viral hemorrhagic fever that killed 15 miliion people in Mexico and Central America.
Great Plague of London 1665 - 1666 this was the last major outbreak of the Black Death and killed 15% of London's population.
Spanish Flu 1918 - 1920 infected an estimated 500 million people and one fifth of these died. Its spread and fatality was made worse by the conditions of soldiers in WW1. It didn't actually start in Spain - Spain's neutrality in the war meant its press could report freely on the disease and people thought the disease was specific to Spain.
Asian Flu - 1957 - 1958 started in China this killed more than 1 million people and was a blend of avian flu viruses.
AIDS 1981 - present day HIV the virus that causes AIDS was likely a chimpanzee virus that transferred to humans in West Africa in the 1920s. Estimates suggest that 35 million people have died from AIDS and about 64% of the estimated 40 million people living with HIV live in sub- Saharan Africa.
H1N1 Swine Flu pandemic 2009 - 2010 this originated in Mexico before spreading to the rest of world, infecting 1.4 billion people and killing between 151,700 and 547,400 people, according the the CDC.
Ebola 2014 - 2016 In West Africa there were 28,600 cases reported and 11,325 deaths, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. There is no cure for Ebola and it is thought to have originated in bats.
Zika virus 2015 - present day spread by mosquitos mainly although it can be spread through sexual intercourse, this attacks infants in the womb and causes birth defects. It is found mainly in South and Central America and in the southern US states.
"Crimson Contagion" this was an (imaginary) exercise carried out in 2019 by the US Department of Health and Human Services which postulated a flu pandemic caused by a novel virus starting in China and spreading round the world, predicting 586,000 deaths in the USA alone.
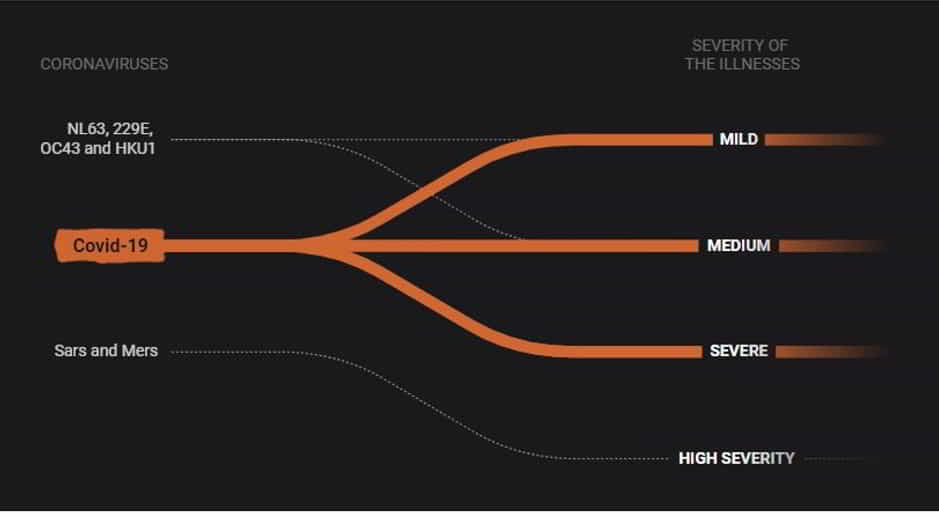
What is the Coronavirus
This scrolling infographic from the South China Morning Post (SCMP) goes through different types of coronaviruses, explains how they spread and how they affect humans.
It opens in a different window - click on the image then scroll down.
In December 2019 the world was introduced to the word Zoonotic; Pertaining to a zoonosis: a disease that can be transmitted from animals to people or, more specifically, a disease that normally exists in animals but that can infect humans. There are multitudes of zoonotic diseases.
In 2003 the Chinese government confirmed SARS originated in the meat markets of China. The government banned the illegal markets and 12 months later they all started up again.Covid-19 is a version of SARS and has mutated over 16 years but this time it’s more infectious.
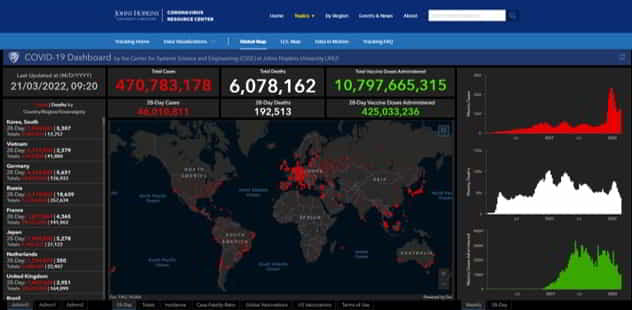
What's the current position with Covid-19?
This real time dashboard from John Hopkins University has the latest numbers for COVID-19 cases, deaths, recoveries and more. It’s sorted by country and state and updates in real time.
It opens in a different window – just click on the image and bookmark the page!.
There's some info on death rates below - when we looked at this dashboard we saw the deaths: cases ratio for the UK was 0.83%.
The Financial Times also has a Coronavirus Tracker – normally only open to subscribers but available to anyone, which gives a constantly updated view of the effects of the pandemic.
It allows you to compare countries (for example, the cumulative deaths per 100K people since 1/1/2020 attributed to Covid-10 in Sweden which had no lockdowns is two thirds the rate in the UK).
It also shows excess deaths — the numbers of deaths over and above the historical average — across the globe, and again per million people Sweden’s rate is about 2/3rds that of the UK.
Let’s see what we can do to stay safe. And enough doom and gloom – see the tabs below for more info – the last few are light-hearted impacts from the recent lockdowns.
What is long Covid?
Most people get over Covid recover completely in a few weeks. Others get symptoms that last for weeks or months after the infection has gone. This is called post-COVID-19 syndrome or “long COVID”.
The virus can damage the lungs, heart and brain, which increases the risk of long-term health problems.
How ill you are when you get the virus doesn’t seem to affect whether you get long term symptoms.
Common long COVID symptoms include:
extreme tiredness (fatigue), shortness of breath, chest pain or tightness, problems with memory and concentration (“brain fog”), difficulty sleeping (insomnia), heart palpitations, dizziness, pins and needles, joint pain, depression and anxiety, tinnitus, earaches
feeling sick, diarrhoea, stomach aches, loss of appetite, a high temperature, cough, headaches, sore throat, changes to sense of smell or taste, rashes
Click on any of the tabs on the right to see more information
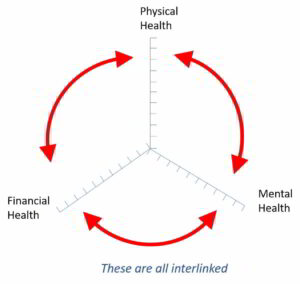
Keep physically active
Especially while staying at home, it’s important to keep physically active to help keep us healthy at this time. Being physically active can not only help keep us healthy physically but can also be good for our mental health.
Looking after your mental health while staying at home
In these times of uncertainty, it’s really important to take care of your mind as well as your body. Having good mental health helps us relax more, achieve more and enjoy our lives more.
See further more detailed advice in other tabs.
The World Health Organisation say that clean hands protect against infection. This is an extract from their page.
They say that to protect yourself you should:
- Clean your hands regularly
- Wash your hands with soap and water, and dry them thoroughly
- Use alcohol-based handrub if you don’t have immediate access to soap and water.

How do I wash my hands properly?
Washing your hands properly takes about as long as singing “Happy Birthday” twice, using the images shown.
It’s really important to take care of your mind as well as your body if you are self-isolating because of coronavirus (COVID-19).
It’s natural to feel worried or anxious about your finances or job, your health or those close to you. You may also feel bored, frustrated or lonely. It’s OK to feel this way – the chances are this will pass. There are things you can do to help yourself through this.
Do Things You Enjoy – distract yourself by catching up on the things you never have time to do – going for a walk (while you can!), reading, bingeing on a box set, or learning something new (see ChangeDrive for some ideas).
Plan things that matter – work out how to get deliveries of what you need, order stuff by phone or online. Create Your Own Schedule: This means setting up a routine. Include all the things you should do and some free time too.
Keep in touch – make sure you stay connected – by phone, messaging, video calls, even social media. Talk to someone you trust about any worries you have.
Try and stay positive – control negative feelings and concentrate on what you can control. Reframe negative thoughts – see the next tab!
Stay away from negs – Limit your news watching to say twice a day and decide in advice which sources you will look at – say WHO and NHS – avoid that spiral of depression. Block people who are repeating misinformation or ‘fake news’ and turn off your phone’s news notifications. Talk to someone you trust who is balanced. Find quiet time when you need it, even if cooped up with family.
Eat well and sleep well – cooking is a good distraction, so try and eat healthily (see FoodDrive). Wind down in plenty of time for bed, and don’t look at the news late on.
Stay Physically Active – as part of that schedule, put time aside at regular intervals for some exercise – in your own home and garden if necessary. See FitnessDrive for some ideas. Yoga is good for the mind and body – look on YouTube even if you’ve never done it before.
From the Mayo Institute
Feeling sad or down: Life can be like being in a boxing ring where you cannot get out, you try not to get punched but if you do get back up and learn to keep out of the way! Solution: talk to others first, think it through but don’t rush for a solution. We have all felt this way on a regular basis its life.
Confused thinking or reduced ability to concentrate: When you have a lot going off in your life there are times when we suffer this effect. Stop and step back and talk to others. If it persists for a long time you need to look deeper.
Excessive fears or worries, or extreme feelings of guilt: At times we all have these and it’s natural to worry about things that are really important. The word extreme means different things to different people so you need to talk to someone else and gauge if it is extreme, if in doubt seek professional advice
Extreme mood changes of highs and lows: These also can happen in everyday life and they are perfectly normal. We may have inner calm but there is always someone that wants to burst our bubble – the glass half empty brigade. If they become very extreme talk to others, you will be surprised how often it happens to them too.
Withdrawal from friends and activities: As we develop in our lives our feelings, emotions, thoughts change. We may move, change jobs, or move house. Managing change is a skill and we need to be aware of how to do it. Often the older we get the more cynical we become but withdrawal from society totally isn’t a good thing. Humans need interaction whatever that might be. So, managing this is important. Living in a tree isn’t good for your soul.
Significant tiredness, low energy or problems sleeping: Getting a good night’s sleep is really important, but if you’re worrying about things or feeling tired you could be using lots of mental energy.
Detachment from reality (delusions), paranoia or hallucinations: To some degree detachment from reality and delusions are common in humans; we see it in everyday life, on the TV, in the media, social media etc. If someone has a dull life, they are naturally going to look for an escape. Talking honestly to people about how we feel can help. Extremes here are a problem and you need to seek professional advice.
Inability to cope with daily problems or stress: This can be the effect of a life that is going wrong. We all know people who seem to have a car crash life and wonder why. If our work/ homelife / social life is extreme then it can cause stress. We need to take a step back, talk to others or in extreme cases seek counselling.
Trouble understanding and relating to situations and to people: This happens to everyone sometimes, it’s called life. How to manage it is talk to others, try to judge how strong your issue is then deciding on a course of action.
Problems with alcohol or drug use: Alcohol envelops your life eventually and reduces your ability to take personal responsibility. There are many support functions online.
Major changes in eating habits: Usually this is an effect of something deeper going on. If you start to put lots of weight on don’t let it get out of control – excessive drink and eating will create even bigger health problems. If you see others ballooning don’t be frightened to speak up and say.
Sex drive changes: To some degree this is life – it happens as we age or life circumstances hit us. Our body and brain cannot always deal with all life issues and focus normally on sex drive. Again, step back, self-analyse, don’t rush to judge. The internet is full of information or if you can talk to someone else to see how much of a problem it is.
Excessive anger, hostility or violence: We can all feel anger and hostility towards life, others, things but violence is a different matter. Once we start to step into violence then we need medical help.
Suicidal thinking: People who are at the stage of wishing to end their lives need medical counselling and support immediately.
Clearly isolating causes different types of stress on a relationship, especially with children being at home constantly too.
This is a light-hearted look at how people’s reactions to the current position are putting us in to different camps. These examples are all drawn from friends and family of YouDrivers!
Different Types of Response
People seem to be reacting in number of different ways:
Heroes – we don’t just mean NHS staff, retail staff, delivery drivers, etc. Some people are going above and beyond – helping more vulnerable people. Groups have been set up taking orders, dropping the supplies outside and settling up when this is all over.
Dipsticks – hoarding toilet rolls (an offshoot of self isolation combined with too much internet access?), pushing NHS staff out of the way in supermarket queues, coughing on emergency workers,…
Pragmatic – follow WHO guidance, self isolate as much as possible, social distance, only buy essentials (not boring really!)
Chilled – some people think it’s no worse than ‘flu, or it only affects the elderly, or they’ve seen worse. Oddly includes some older vulnerable people – “I’ve lived through worse – SARS, etc”
Jokers – the constant stream of pictures, videos, social apps, remote parties, quizzes and games is keeping spirits up (good job with no sport or concerts or pubs or….) – this post is for and because of you!
Of course now we’re stuck in our households, if there’s more than one type there could be trouble – “irresponsible” versus “nagging”! That’s always a good start for arguments!
Even for married couples who are ’empty nesters’, there can be problems when the normal routes of escape are blocked. People who used to escape fishing now risk being stopped by police and asked whether their journey is necessary. Explaining the significant risk of death (by murder) as the alternative probably won’t work.

You may remember this ‘survey’ video…
I think after a week’s home schooling my kid is up to something….

Being at home with (several) young children who are normally at school / at nursery / being looked after by someone else can be VERY stressful. Especially as you can’t easily take them out to make sure they’re tired.
Remember when you had to queue to get in to the supermarket, and when you got there half the shelves were empty anyway. For some reason there were always chickpeas. What are they for?

We’re not sure about anyone else, but we YouDrivers have put on weight over the last couple of years.

The combination of social distancing, lack of supermarket delivery slots, difficulties getting into shops, 3 item limits, enforced time with limited people could be bad and lead to arguments….
Although infidelity will be seriously reduced, there will be long term health side-effects…


What did governments do?
Initial assumptions
It's fair to say that a lot of assumptions made initially were, well, just plain wrong. Some things that were regarded as mad anti-vax conspiracy theories have now been accepted as fact by the WHO. When we initially created EpidemicDrive we put:
"Once you’ve had the disease and recovered, it’s believed you have immunity and don’t get sick or pass it on. Ideally once enough people have had the disease, we develop ‘herd immunity’ where enough people don’t get the disease and it dies out. "
Now we know you can catch the disease after being vaccinated and boosted, and also pass it on. The fourth dose is now being made available to the vulnerable.
Governments reacted to the situation in Italy, where it looked as though the health service would be overwhelmed. Social distancing was introduced, masks were / weren't / were made mandatory and lockdowns were introduced, and a race to create effective vaccinations started. Interestingly Sweden didn't introduce a lockdown - because their constitution did NOT allow the government to make the decision - it was made by their chief epidemiologist Anders Tegnell.
The first reaction almost worldwide was lockdown. China tried Forced Quarantine Hubei province. Social Distancing is avoiding public gatherings, staying at home and keeping a distance from others. It can be applied to a moderate group of people or more extensively – some people will always have to do key jobs.
The problem is that enough people get sick at the same time the Health Service can’t cope and we see the pressure like there was initially in northern Italy, and people die.
The Washington Post has a great interactive page which allows YOU to model these different approaches and see what the different outcomes are. It shows the numbers of people healthy, sick and recovered and how these change over time in different scenarios. Try it here – it opens in a new window – scroll down and have a look.
To summarise, it models a fake disease which spreads even more easily than Covid-18 through a population of 200 people; when a healthy person comes into contact with a sick person, they get sick. When they’ve recovered, they can’t catch it again nor transmit it. The chart below shows the results of free for all movement, forced quarantine, 3/4 of people social isolating and 7/8ths of people social isolating.
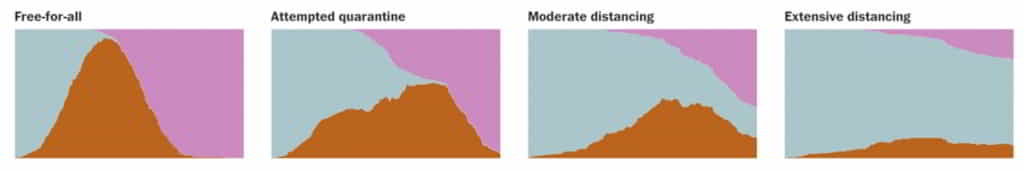
Grey is healthy people, brown is sick people and pink is recovered people. You’ll see the ‘curve’ of people getting sicker is higher in the first two simulations.
How effective are Lockdowns?
You may have seen a ‘John Hopkins study’ which has been doing the rounds on social media? We have to admit that sadly we were taken in by it initially!

It actually isn’t from the University as such – it’s a working paper by a Professor of Applied Economics at John Hopkins and two other professors from Denmark and Sweden.
However, there’s a paper titled: Lockdown fatigue: The declining effectiveness of lockdowns from Patricio Goldstein, Eduardo Levy Yeyati, Luca Sartorio on VOX EU / CEPR dated 30 March 2021 which does show that : “Initially, lockdowns are associated with a significant reduction in the spread of the virus and the number of related deaths, but this effect declines over time. Lockdown does not work as a continuous containment policy in the event of a protracted pandemic.”
What's the death rate?
"The death rate of the coronavirus is difficult to measure. At the time of writing, there have been 40,636 deaths from 923,470 confirmed cases around the world, or 4.9%. This compares with a death rate for seasonal flu of 0.1%
The figure is hopelessly unreliable, depends on what we’re measuring and varies hugely from country to country. We don’t really know:
- how many would have died anyway
- how many people have been infected with only mild symptoms and not counted
- who has been tested
- how old the infected people are
- the way the country report the cause of death
Note that in the UK about 150,000 people die every year between January and March – the vast majority who have died have been over 70 or had a pre-existing condition."
Since then we know a lot more about these factors. The chart on the right is from Our World in Data (click button to go to site) and shows the case mortality rate - see the tabs below for other measures.
Click on any of the tabs on the right to see more information
There are analyses available to show how the number of people dying has varied from normal since the start of the pandemic.
Excess mortality is a term used in epidemiology and public health that refers to the number of deaths from all causes during a crisis above and beyond what we would have expected to see under ‘normal’ condition
The Office for Health Improvement and Disparities have a detailed analysis you can download, and the overall view at mid March is shown below.

This shows excess deaths above normal in the first and second wave of the pandemic. Indeed, there were more than 695,000 deaths in the UK in 2020 – more than any year since 1918 and the Spanish Flu pandemic.
Excess mortality is a term used in epidemiology and public health that refers to the number of deaths from all causes during a crisis above and beyond what we would have expected to see under ‘normal’ conditions.
Our World in data have a detailed analysis you can look at, and the excess mortality P-scores [(Reported Deaths – Projected Deaths) / Projected Deaths is shown for Russia, USA, UK, Sweden France and Germany.

This shows excess deaths in the UK was higher than all in the first wave, but has been lower since.
The case fatality rate (CFR) is simply the number of confirmed deaths divided by the number of confirmed cases.
This chart shown above plots the CFR calculated in this way.
When the number of actual cases and deaths is not known – as is the case for COVID – one has to be careful in interpreting the CFR. On the website it explains what we can and cannot learn about the mortality risk based on the CFR.
The crude mortality rate – sometimes also called the crude death rate – measures the share among the entire population that have died from a particular disease. It’s calculated by dividing the number of deaths from the disease by the total population. For instance, if there were 1,000 deaths in a population of 1 million, the crude mortality rate would be (1,000 / 1,000.000), or 0.1%.
The crude mortality rate isn’t particularly applicable DURING a pandemic. In an article analysing New York data the crude death rate was estimated to be 0.28%, but this will increase.
The IFR is the number of deaths from a disease divided by the total number of cases. If 10 people die of the disease, and 500 actually have it, then the IFR is (10 / 500), or 2%.
So the IFR answers the question: if someone is infected with the disease how likely is it that they will die from it?
The problem with Covid-19 is that we don’t know the total number of cases.
Again the data from New York suggested the IFR was 1.4%.
The CFR differs by region and by time. As things change and the disease mutates things change.

In the chart above, (Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) the CFR for COVID-19 from the beginning of January to 20th February 2020 the CFR was much higher: 17.3% across China as a whole (in yellow) and greater than 20% in the center of the outbreak, in Wuhan (in blue).
But in the weeks that followed, the CFR declined, reaching as low as 0.7% for patients who first showed symptoms after February 1st. The WHO reported that that was because “the standard of care has evolved over the course of the outbreak”.
The case fatality rates for other disease outbreaks are:
SARS-CoV 10% Venkatesh and Memish (2004)
Munster et al. (2020)
MERS-CoV 34%, Munster et al. (2020)
US seasonal flu has a case fatality rate of approximately 0.1% to 0.2%.
Ebola has a CFR of 50% – 40% in the 2013-16 outbreak.
WHO (2020)
Shultz et al. (2016)

So what's changed?
The pandemic and the world's governments' reactions to it have changed the way we look at things. The restrictions to personal freedoms, whether for better or worse, would never have even been considered ten years ago, and we are still not fully out of it.
The world has changed - so let's look at some of the ways it has changed, and whether it's for better or worse.
Click on any of the tabs on the right to see more information
The world is changing!!!
For the better or for the worse? Who knows?
I am sure there are millions of views on the subject based upon your own life’s view.
Let’s start by talking about change – we have seen change programmes working well and badly. There are generally two types of change; evolutionary and revolutionary.
Both work and both have upsides and downsides. With evolutionary change you have the ability to take a slower more controlled approach, and manage events or issues arising as a result of the change. With revolutionary change there is always unpredictability and you cannot always foresee the outcome, or manage issues arising from the change.
The boom years
Over the last 30 years it could be said that the pace of change has been quite revolutionary. There has been a population explosion, wealth increases, housing booms, materialism spiking, obesity increasing and personal greed abundant. The pre- and post-millennium years are seeing a new type of person, who has not seen deprivation, poverty, wars etc. The 80s and 90s saw a major leap in the internet and 00s saw social media storm into our lives.
Our liberal societies have created a different way of living – tolerance all round and a greater understanding of people’s rights. Due to the feel-good factor years of the 80s and 90s it could be said children were pampered and given far more than ever before. We told all children they could be whatever they wanted in life, and they did not experience any real hardship or disappointment.
Instant coffee
Today there is an instant coffee, DFS buy now pay later philosophy, get rich easy mentality and a celebrity culture. We want everything yesterday and our desire for greater choice in all aspects of life. We used to save for things we wanted – now we get them on credit, which has led to constantly increasing personal indebtedness.
The suppliers have capitalised on this by accelerating our choices and options and offering more and more things for us to buy and use. The throw-away culture particularly in the UK and US is now part of our everyday life.
Life is moving quicker; improved transport and communications links mean the world is now one marketplace like never before. Goods and services are open to world markets and financial sectors are all linked. 50 years ago, a country could have a problem and nobody found out. The macro communications of today means the smallest of information is available every second of every day, and on your phone.
Our souls are peddled around for profit
Media and marketing have never been so dominant as they are today with big data and your soul passed around from company to company to persuade you to buy or influence your opinion. Media feel now they play an even bigger role in persuading you or moulding your opinion on everything in life. Often sitting behind this there are companies and individuals making money out of their action.
Opinions are also now more public and the centre ground seems to have disappeared. We now have rigid views and even the smallest of things get debated and discussed, with extreme views on either side of a divide. Brexit seemed to divide the nation from 2016 to 2020 and people on both sides of the argument had extreme views but there hasn’t been a word about Brexit since the Covid-19 outbreak.
So strong are opinions now that the situation has become almost tribal with people hating each other for holding a different view. Often it can be over the most trivial of things.
I apologise for everything I’ve done and more
If a person says anything today it seems that someone or somebody is offended and demanding an apology. People who hold strong historical values in any area appear to be classed as ISTs.
In 2019 Extinction rebellion have been highlighting the issue with the climate and to get us to focus on climate change. They are seen as extremists to many and heroes to others. But their methods might not be for everyone but their message is clear. This planet is ours; humans are the most intelligent creatures and responsible for the balance and ecosystem.
Many people thought at the time, go and protest in countries that are the worst offenders; see how far you get before you get locked up. But these countries are often supplying the more advanced west.
The dynamics of change have consequences
In 2018 we saw the longevity indicator change for the first time since the 50s. This means currently today’s grandchildren will not outlive their grandparents and this is totally down to lifestyle. We are seeing personal indebtedness the highest ever as people borrow more to have things they want now and not save and buy later. Obesity in the UK is rocketing out of control and we are eating ourselves into coronary issues, type 2 diabetes and spinal issues due to our excess weight. We have seen a dramatic increase in recorded mental health issues especially in the millennials.
Then the Coronavirus arrived
In December 2019 The outbreak of Covid-19 came and for the first time since WW2 Society has been forced to change its whole lifestyle and for the adults born since 1980 this is something completely new; a state enforced lockdown, a change of liberty and being told what to do and when to do it with legal consequences if you fail.
It’s interesting to note that when you are faced with such an issue how those previously previously hot topics seem to pale into insignificance.
What are the British views and attitudes towards the Coronavirus and the government’s position? The information below was published in mid 2020 – it is interesting to see how much still applies now.
As we said at the beginning of this post, a YouGov poll just before and just after the PM’s speech putting the UK in lockdown showed most people (58%) agreed with the government’s stance.
However, people thought the public WEREN’T taking it seriously.

People are afraid
Although most thought they’d be OK, one in three people said they’re fearful for the future (more women than men). The YouGov poll showed.
At that time half of Brits felt that the virus would kill millions worldwide, but 31% felt it wouldn’t be much worse than a typical flu.
Changes in Society
You need to scroll down to see all the info in this popup – sorry for going on so much!
How does society react to change?
There’s no simple answer to this. There are some trends – for example, some social attitudes and policies have become more inclusive – such as in gender equality, whereas some have hardened – such as the people’s support for or against some ideas – such as climate change, Brexit or Scottish Independence.
Several studies are looking at what is causing these views – is it age, life experience, etc.
Understanding Society is a UK Household Longitudinal Study that interviews everyone in household to investigate information on changes in society. These surveys started as The British Household Panel Survey in 1991 and continue now.
They cover some interesting points and examine how people’s attitudes and views have changed. We give a few extracts below that we think are important.
Religion
The surveys show that there is a continuing long term decline in religious identity, observance and belief in Britain.Back in 1983 teo thirds of the British public identified as Christian – it is now just over one third with 53% saying they do not see themselves as belonging to any religion. In fact, more people are now positively atheist, with one third now saying they don’t believe in God as opposed to 10% in 1998.
Brits remain tolerant of religion, particularly Christianity, but we are sceptical about its role in society. Almost two-thirds (63%) of the British public agree that religions bring more conflict than peace (28% strongly agree”, 35% “agree”) – while only 13% disagree (10% “disagree”, 3% “strongly disagree”).
Science
People believe more in science than before; only 11% of people now think that science does more harm than good – it was 24% in 1993.
- 77% public agree science is making our lives healthier, easier and more comfortable
- 94% believe medical research will improve our quality of life
Most people trust scientists to work in the public interest – university scientists (85%) more than commercial scientists (67%).
Relationships and Gender Identity
Interestingly belief in the ‘common law marriage’ of co-habiting couples still exists, although it has no basis in law. Opposite sex civil partnerships which were introduced in October 2018 are supported by two thirds of people – more from people who don’t identify with religion.
Attitudes to transgender people are interesting. Most people (83%) say they are “not prejudiced at all” towards transgender people, but half (49%) view prejudice towards transgender people as “always” wrong.
Politics
Like religious belief, identification with traditional political parties has declined. In 1987, 44% described themselves as a “fairly strong” or “very strong” identifier with a political party, while today it is 35%. The relationship between social class and political parties has weakened and other factors such as age, education and degree of liberalism have become more important.
Age is a big factor, with Labour support being far higher in younger voters and Conservative support higher amongst older voters.
Brexit and the EU
The 2016 referendum created a new ‘fault line’ in British society – Leavers and Remainers. These identities in 2019 commanded significantly stronger allegiance than traditional political parties, with 74% of the public describing themselves as having a “fairly strong” (34%) or “very strong” (40%) identification with either Leave or Remain, and just 12% who do not identify with either. Only 8% say they are a “very strong” supporter of a political party.
Concerns about the social consequences of EU membership were key in influencing how
people voted in the EU referendum. More people who were worried about immigration and held ‘authoritarian; (rather than ‘libertarian’) views voted to leave. Multivariate analysis found that, for the most part, only items associated with people’s sense
of national identity and cultural outlook were significantly associated with vote choice. So the common view that dissatisfaction with politics influenced how people voted wasn’t found to be true.
The surveys worked out people’s attitudes to the EU by asking:
Do you think Britain’s long-term policy should be…
…to leave the European Union,to stay in the EU and try to reduce the EU’s powers,
to leave things as they are,
to stay in the EU and try to increase the EU’s powers,
or, to work for the formation of a single European government?
Until 2008 less than 20% thought Britain should leave the EU, but by the referendum three quarters (75%) felt that Britain should either leave the EU or that if it stayed the institution’s powers should be reduced.
After the referendum, Britain became MORE divided in its attitudes to leaving the EU.
Immigration
From 2002 to 2014 the public has become more positive about the benefits of immigration, but more selective on who they wish to migrate. They are also slightly more sceptical about the cultural benefits of immigration. However, there has been little shift on views of migrant numbers. This is also true in Europe.
YouDrive note: It is surprising then that over the last three decades far right parties have tripled their vote share across Europe from 5% to 15%. Political scientists say that the single most important reason why people vote for far-right parties is their attitude towards immigration. Yet people’s attitudes to immigration haven’t changed.
This could be due to far right parties becoming closer to traditional parties, voters becoming less attached to a particular party or the news focus on immigration and the refugee crisis.
Mental Health
People’s willingness to work, live and continue a relationship with someone with a mental health problem have improved by 11% since 2009 – from the National Attitudes to Mental Illness Survey. Time to Change is a mental health campaign and since it started in 2007 4.1 million people have improved attitudes towards people with mental problems.
Social Care
Most people (86%) agree with policy makers that people over-use A&E and 999 ambulances. Part of this problem is that 51% of people say it is difficult to get a doctor’s appointment. 36% prefer NHS services where no appointment is needed, rising to 48% of those living in deprived areas.
There is scope to increase the use of online tools (such as YouDriveHealth!) to help tackle high demand. 58% of people with internet access would look online to help understand a health problem and 47% would use the internet to decide what to do about it.
The Covid-19 pandemic has put even these online services under strain. Recently a YouDriver struggled to find support for a friend undergoing mental health depression issues, either online or by phone.
From ipsos:
A new Ipsos survey for the World Economic Forum finds that, on average across 30 countries, 71% of adults do not expect that COVID-19 will ever stop spreading entirely. A majority of adults in every country – from 51% in China to 85% in the Netherlands – agree that “even with all the measures being taken, we will never be able to fully stop the spread of COVID-19 and variants.”
Opinions on compulsory vaccinations vary:
In Asia and South America more than 75% support making vaccination mandatory, while in the US and most of Europe people are opposed to it, although support for mandatory vaccination has grown in China, Italy, Australia, Germany and France, but decreased in Japan and USA.
What would you do if you tested positive for Covid?
An ipsos poll in February as the government relaxed restrictions showed what people would do if they tested positive for Covid.

The enforced changes have made people realise that some things they were doing were just wrong.
This powerful video from Tomfoolery describes some harsh truths about the ways we lived. It’s a very moving video.
Air pollution
he World Health Organisation have estimated that about 3 million people die each year from illness caused by air pollution. It’s worse in poorer countries. Nitrogen dioxide levels have fallen by up to 60% in the UK compared to 2019 in the two weeks after lockdown.

These pictures from Sky News of Hong Kong before and after makes it clear (sic).
Will we become more societal?
So, what’s ‘societal’, and how is it different from ‘social’?
Societal means relating to society or social relations. Social is broader and can mean a society, or a family, or can refer to a person who interacts more with other people (rather than a less social person). Is this why ‘societal’ is becoming a bit buzzy again – people want to be clear that they are talking about things pertaining to society as a whole.
I believe that the coronavirus epidemic is a threat unlike is exaggerated more than anything else
The box below shows some information on exactly how bad the coronavirus epidemic is and why. Hover over it and it will show you some arguments that suggest we are overreacting and that the situation isn’t as bad as is being reported. Click the button on the back to see this second point of view and YouDrive’s thoughts!
The coronavirus is a great threat
The coronavirus threat has been greatly exaggerated
For visitors
Why don't you join us?
You can register to join us as a member, when you’ll be able to download our stuff and comment, or as a YouDriver when you’ll also be able to check your health and set up your own action plans to make some improvements. If you’ve already registered, sign in below. Or let us know what you think.
The Coronavirus explained
The coronavirus explained
this animated video by Kurzgesagt still provides a handy explainer on how the virus works. It’s about 8 minutes long
A TED TALK ON THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
This talk explains more about COVID-19 and how it fits in with the global health system.
How the Coronavirus fits in
Next Steps
It doesn’t matter what stage you’re at – it’s important to be the best you can be. At the end of the day it’s about taking personal responsibility – You Drive!
It’s really your choice. You can find out more information about the subject, or see other institutions that can help by going to Support. There you will find organisations, training, coaching, self-help courses and other items to support your personal change. We have also started developing a panel of experts to provide info, advice, help and support.
Get Support
There are times when you need some help to meet your aims – a helping hand. That might be an organisation that can provide you with some help, some specialised information, a particular book or tool to help, or just getting some background reading material.
We have a lot of items which appear on our Drives and other pages, which you can go to by clicking on the picture or link. Some contain affiliate links and we may receive a tiny commission for purchases made through these links.
If you know of anything which could help you or our other visitors then please click the button on the right, which will take you to a Contacts page where you contact us.
Experts
We are compiling a list of experts who can provide advice, help or specialised services. You will be able to access these experts from anywhere on our site you see our ‘Experts’ symbol. Click the green E to see what our Experts list will look like, with a couple of imaginary ‘experts’ added!
More Information
Scroll down to see more information on this Drive.
If you register you can also download reports, white papers, quizzes and other collaterals. We will never ask you for any financial information, and we’ll only send you the information you want. You can register for our site either above or in the footer below. You can provide your own questions and experiences in order to help other members. We only moderate for spam and inflammatory language – see our moderation policy.
If you’ve found this interesting, then please share it on social media. Choose your network!
More information
Corona, False Alarm?
Facts and Figures
In Corona, False Alarm?, award-winning researchers Dr. Sucharit Bhakdi and Dr. Karina Reiss give clarity to these confusing and stressful times. They offer analysis of whether radical protective measures, including lockdown, social distancing, and mandatory masking, have been justified, and what the ramifications have been for society, the economy, and public health.
Covid: Why most of what you know is wrong
In this book, the Swedish doctor Sebastian Rushworth examines some of the most central questions about the Covid-19 pandemic: How deadly is Covid-19? What is long Covid? How accurate are the Covid tests? Does lockdown prevent Covid deaths? and many more
CRISIS, CULL or COUP?
WHAT, HOW and WHO? Facts and Truths to Make You Think!: Exposing The Great Lie and the Truth About the Covid-19 Phenomenon.
So, you want to know what’s really going on? Are you ready for the shocking truth? An inconvenient truth that requires each and every one of us to take individual and collective responsibility in the face of what may yet prove to be the greatest orchestrated crime against humanity that the world has ever seen.
NHS provide information on coronavirus and advice on symptoms and self isolation
The government publish daily information on the number of cases and more information
The NHS as part of their every mind matters provide advice on maintaining mental wellbeing during this time
The World Health Organisation provide a global update on the coronavirus epidemic
This world map by John Hopkins University is updated daily and has many worldwide facts
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control have information you can see and download on Covid